Can STD Cause Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer and is caused by the HPV virus. The human papillomavirus belonging to the papillomavirus family of viruses can be passed from one human to another through genital contact, vaginal or anal sex and in some cases through oral sex. Commonly the virus goes away without any severe health effects but in some cases it can lead to modification of normal cells into abnormal cancerous cells causing cervical cancer. It is most common in women and develops around the uterus and vagina. It can lie dormant for several years and can easily go undetected.
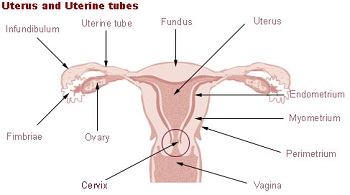
The Pap smear test is the most common test for detecting pre-symptomatic stages of cervical cancer and can help in early detection and prevention of cervical cancer. This test is cheap and can be done in many hospitals. Women are encouraged to take this test every 5 years and maintain healthy sexual contact throughout their lives. Negligence on the part of sexual partners can easily lead to one transferring the virus to other.
The HPV virus exists in about 100 different strains and two of them 6 and 11 produce very painful genital warts. About 70% of people come in contact with the HPV virus in their lifetime. Warts are clot like structures and can be a big nuisance. They are one of the symptoms of HPV that can be visibly diagnosed. Many other forms including the deadly strain 16 can go undetected in early stages and cause half of the cancer cases.
Though a deadly disease HPV is very different from HIV in terms of symptoms and effects. HPV virus unlike the HIV virus lives on the skin cells. The HPV virus can cause various health problems like genital warts, cervical cancer or Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis (RRP). As is always said prevention is better than cure. HPV vaccines should be given to children of the age of 11-12years. These vaccines are completely safe and effective. With our current generation getting proper knowledge of AIDS and STDs. Knowledge about the HPV virus is equally important amongst youngsters. People should take necessary precautions while having sex and limit their partners to avoid infection. Condoms cannot completely protect you against HPV as it is caused by physical contact of genitalia.
Yes STDs can cause Cervical Cancer and everyone especially women should undergo regular tests throughout their lifetime and lead a healthy sexual life to avoid this disease.
Do Anti-Aging Creams Really Work?
If you’ve ever tried an expensive anti-wrinkle cream, only to find it didn’t give you the results you hoped for, then you’re not alone. Millions of people try these products every day, only to find they they are no superior than their everyday moisturizers.
But does this mean all anti aging creams are a waste of money? Not at all. In fact, recent developments in skin care science mean there has never been a better time to find product that can legitimately reduce the sign of those fine lines and wrinkles. But the secret lies within the ingredients the product uses, and not the over-hyped marketing that many skin care companies take part in.
With this in mind, here are a few crucial ingredients to look out for (if you’re serious about finding something that works).
Retinol
This is the king of anti-aging skin care ingredients. It’s essentially a vitamin A compound that works to create new growth of collagen and elastin. Additionally, retinol is one of the few ingredients which has shown undeniable proof of efficacy in dozens of clinical studies. So if you want a powerful anti wrinkle cream, check the label to see if it contains this crucial ingredient.
Hyaluronic Acid
One of the most common reasons why fine lines and wrinkles develop is due to lack of hydration within the skin cells. Using a topical moisturizer is crucial, but it’s equally important to make sure your skin is hydrated from within. The first step is to make sure you’re drinking enough water each day, and the next step is to make sure your levels of hyaluronic acid are up to par. This ingredient can be absorbed through your skin, and it increases your natural ability to hold moisture inside the skin cell. This can give your skin a younger, plumper, firmer appearance – and it can also help to diminish the appearance of wrinkles.

Unfortunately, many people waste money on anti-wrinkle creams which don’t live up to the hype. But with a little research and insight, it’s possible to get excellent results with over-the-counter creams, just as long as you stick to products which use proven ingredients. In fact, the lifecell wrinkle cream formula contains both of these ingredients, so this is certainly a good option (but unfortunately, it isn’t cheap).
The tips in this article were provided by Rita Brooks, a natural health enthusiast who specializes in skin care advice. Be sure to check out her detailed reviews and natural health guides. You can find her blog at ritabrooks.com
How To Remove Cellulite Using Body Wraps
Cellulite is a problem that most females will experience at some point in their life. For years experts have been trying to identify the true cause of the development of cellulite, but no one knows for sure what actually causes these unsightly dimples to show up on the skin.
Some experts believe it isn’t just one thing that leads to the development of cellulite, but a variety of different factors. Some of the things that can lead to the development of cellulite include diet, lack of exercise, the clothes you wear, genetics, age, and bad habits like smoking.
Regardless of what causes it most women are on the look out for a proven way to get rid of cellulite and keep it from reappearing. There are various options available that can help reduce the appearance of the dimples and bumps caused by this problem. However, anti-cellulite wraps are among the most effective treatment method of them all.
Compared to cosmetic surgery, body wraps are a very cheap way to treat cellulite. These wraps help get rid of cellulite naturally because they have certain ingredients inside them that help draw out the fat toxins that lead to cellulite formation.
First you need to buy a good body wrap. You can find some really good ones on the Internet, but there are also some health food stores you can visit that will have them on sale too. All anti-cellulite wraps are not made the same, as they all contain different ingredients which serves a different purposes.
If you wish to keep your body protected from free radicals that cause cellulite then go with a vitamin E body wrap. If you want to draw out the toxins that are often responsible for cellulite showing up you should go with a clay body wrap. If you notice that your skin has been damaged by cellulite you should invest in an almond oil body wrap, as it will soften and moisturize your skin.
Fluid retention is also a common cause of cellulite, and a body wrap that contains juniper berry will help you reduce fluid retention. A lack of blood flow can also lead to the development of cellulite, which means you should definitely get a body wrap that contains either caffeine or rose oil in it because they both will help improve your blood flow to the problem areas.
Once you have the right body wrap all you will need to do is put it on the affected area on your skin and then your skin pores will start to open up. Once your pores open up the wrap will start to draw out the toxins and fats that are causing cellulite to develop right below the surface of your skin. Until the cellulite is finally removed the fatty tissues will break down gradually.
Even though body wraps are very effective you shouldn’t only depend on them. Follow a healthy diet that includes many green vegetables along with applying the wraps to the problem areas on your skin. Also, you will have to keep on applying the wraps consistently in order to notice your cellulite disappearing.
The fact that body wraps are inexpensive and effective makes them worth paying for. Most women also love using them because they are an all-natural method, they don’t cause any pain when you use them, and they are very easy to use. Probably the best benefit of all is the fact that they don’t cause any adverse effects like some other treatment methods do.
Lecture on Dental Materials P4
So anyone know what amalgam is? It isn’t that way to get that right. One of the components is and you can see why we don’t have so much of this technology any more, mercury. But there was a time when this was the dominant one and probably if you’ve got grandparents or great grandparents, you may even have a scenario where they had silver or gold as their filling, right? So not very cost effective, but it made for a good filling, mostly because it was malleable and inert. So it’s liquid at room temperature, reacts with silver and tin and essentially forms a plastic mass [at times]. So in essence it was the precursor to the bone cement concept, right? You could have something that was workable, shapeable like a dough and then you could plug it in and it would set. So in a matter of moments, you actually had a hard material that was capable of supporting load.
Nickel titanium, which also we call nitinol. So that’s a 50:50 alloy. Gold, again not so common anymore. Probably the acrylic resins at this point dominate. So those are based on polymethyl methacrylate type resin chemistry, very much like bone cement, sets up very, very quickly. Dental works a little bit different from the orthopedics and not — Dr. Reese made a comment about bone cement, I think I made a comment about the bone cements, Dr. Andy Combs made a comment about bone cement, it’s a two-part system, you’ve got pre-polymerized powder and then bring it in except that it’s a chemical hazard to get the monomer in here. You’ve got a monomer that starts that process, you’ve got a liquid vial and then you’ve got a little packet of pre-polymerized powder, put the two together in a bowl, mix it up and you essentially start to dough a mass. So it starts as something that’s almost fully liquid like pancake batter and then ends up something like plateau. And so in a matter of 3 to 5 minutes you move from a liquid to something that feels like plateau. And as it goes through its polymerization process you’ve got a very high temperature increase, so up to 100 degrees or 150 or so degrees Fahrenheit. So it gets so hot you can’t even hold it in your hand any more. So that part of the experiment is great to show the class, it’s the monomer part. So I used to bring it and do in class and I think truly it’s an environmental hazard. So we won’t do that.
Just take my word on it but that same concept really was important but have any of you had filling work in the last few years of any sort? Did you experience that technology? Probably not. So more likely what they did is that they took the same resin chemistry, but they used a UV curable polymer. So more likely they just set something up in your mouth and then a lot of times, they just do UV exposure and this thing sets up in a matter of moments. But they also have quick setting, but yeah, most of us, right, we have our jaws probe tube and probably aren’t seeing anything. But the chemistry is very, very similar to what we’ve seen in orthopedics and the scent is very similar. So if you recall that odor, you can imagine working in the OR, where you’re going to have 12 to 15 packets of bone cement go by. So environmental issues are an issue which probably explains some of the spacesuit technology. You were in surgery recently? Yeah. So they were in full mask, not just for blood contamination, but there’s a lot of — anytime there’s bone cement you have to look at the outgassing of that monomer. So it’s a real environmental concern. It’s really bad. Yeah, you probably weren’t suited up with that protective gear, yeah.
So if you go and watch a surgery, just be prepared for the other side of that. Actually if any of the nurses are expected, I believe they have to leave the room, it’s that bad. Yeah, so it’s a – there are some downsides of medical technology.
Okay. Thermal expansion coefficients, so like I said, it’s the only place in the class where there is an opportunity to talk about thermal stresses because we really don’t have to deal with that anywhere else. Just a simple analysis, here’s our thermal expansion coefficient alpha, which is the length change delta L, normalized by the initial length for a given temperature. So what that means it is we’re looking at a structure for simplicity sake, which is L0, we subject it to a delta T and then moving through that delta T, we get a coefficient of thermal expansion. So there are only a few scenarios where we have materials that give us a negative thermal expansion. So for the most part we apply delta T, that temperature increase, we move from L to a deformed or expanded length L and so it’s alpha is our change now. So this essentially is this differential here, so it’s the total length change delta L normalized by the initial length L0, multiply that by delta T. And the strain that we get as a result of that – and again we’re assuming isotropy. So isotropy is assumed, the way to get around that would be to do this directionally, right? So just take different orientations and then you could get thermal expansion efficient in a longitudinal axial or circumferential direction.
So the strain is just that thermal expansion coefficient times the delta T. And we look at the biometric thermal expansion coefficient we’ve got the biometric strain, which is three times alpha. So again just alpha coming back to give us deltal L over L0 times delta T. So just a very simple expression.
And I gave you on this worksheet that you downloaded, what happens as a result of thermal expansion coefficient? So it’s a really simple problem. It’s not to show dissimilar the schematic that we have here. Not so dissimilar from what we had when we talked about transferring stresses or looking at composite type behavior. So we’ve got an internal structure, which is in gray. That’s our filling and we’ve essentially reamed out a hole in the tooth structure. So we’re going to assume that we reamed out a nice cylindrical hole. So again you’d have to account for what the geometry is of the hole itself and so we considered here a 2 mm diameter hole, which is 4 mm in length in a molar tooth. So we’ve got a hole that we’ve created, that’s got 2 mm diameter and it’s sitting in a tooth structure. So here is our tooth but we’re just going to schematically say well, it’s got a boundary and we’re going to be [interested]. So we’ve got a diameter of 2 mm and we’ve got a length of that hole which is 4 mm.
And then we look at what’s going to happen to the coefficient of thermal expansion? So in other words, what’s going to happen if we think about this rigid boundary of the tooth acting on this material? So we’ve got a void space and then we’re going to fill that void space with a material. And then we’re going to subject it to a temperature fluctuation, delta T. And then the question is what’s going to happen to that structure? Well, there’s going to be a thermal expansion of that material as it’s heated and then we have to look at thermal expansion mismatch between the enamel itself and the amalgam or resin. So we’re going to just treat this as enamel, and this is going to be our amalgam or resin. And we just look at the difference between the two.
So this basic problem looks at what happens with the delta T at 53 degree C? So we’ve got a delta T of 50 degree C and then we’ve got different thermal expansion coefficients. So we’ve got the thermal expansion coefficient of the amalgam, so there is our mercury alloy of 25 times 10 to the minus 6, again this is millimeters per millimeter. So it’s a length change per original length per degree C. So it’s unit less per degree C or strain units per degree C or strain units per degree C, alpha of enamel. So again a very small thermal expansion coefficient, which probably makes a lot of sense if we think about what thermal expansion coefficient means. So enamel will be a highly ceramic structure. So we’ve got very little exchange of strain as a function of temperature, so only 8.3. And then you look at the polymer, so again we think back to what polymers were, they were these open structured chain materials that are isotropic for the most part, but they’re also randomly organized in space. So there is lot of room for expansion.
And so even though these are somewhat rigid polymers, you’ve got a coefficient of thermal expansion here for a typical acrylic resin on the order of 81 times 10 to the minus 6. So 81 versus 25 versus 8.3. And then you look at – okay, well what’s the elastic modulus of these materials? So the elastic modulus of that alloy, so again steel versus a polymer, the amalgam is 20 gigapascals for elastic modulus. The resin is two and a half gigapascals, so again a much smaller elastic modulus, it’s a polymer. And then we go back to our expression for what’s the change in volume. So again the volumetric strain took the form of three alpha times delta T, right?
So the volumetric strain took a form of three, so we look at delta V, so that was our volumetric strain, when we look at delta V we’ve got whatever the initial volume is and then we’re multiplying that times – three times alpha times delta T. So we’ve got change in volume is the initial volume times three times thermal expansion coefficient and it’s assuming isotropy times delta T. And then you plug this in, and say, well, what’s going to be the change in volume if we use the mercury-based amalgam? So again just geometry, what’s the cross-sectional areas? We’ve got pi times the radius squared. So pi times one millimeter squared times the length, so we’ve got 4 mm of length, then we’ve got three times that difference now in thermal expansion coefficient. So we’ve got 25, which came from the amalgam, and then we subtract away 8.3, so we subtract away the thermal expansion from the enamel, that was to — 10 to the minus 6 power times the temperature flux 50 degree C. And so you get a volume change of 0.03 mm cube.
If you do the same thing for the resin, so again the same geometry would be pi times one millimeter squared, piR squared times the length 4 mm times three, and then the difference would be instead of having 25 minus 8.3, I’d have 81 minus 8.3, same temperature. And so now the volume change is 0.14 mm cube, so relatively large volume change. If I look at just a one-dimensional force span, you’ve got the forces of the elastic modulus times the strain times the area. So you’ve got the elastic modulus times delta T so that 50 degree C times the change that we have on the amalgam resin minus the enamel. So the difference between thermal expansion coefficient, whether it’s the amalgam or whether it’s the resin and subtract away from that the enamel and then you’ve got the perimeter of your pi DH, there’s your diameter, the height. And so you roll that out and you look at the forces and the amalgam force is 420 Newtons, the force in the resin is 228 Newtons. So the forces are relatively high.
But an interesting thing that I put here in gold is that although the resin expands, so if we look at just the delta V, you’ve got a fourfold increase in volumetric expansion. But the reduced stiffness actually results in a lower force. So again it goes back to — you can’t just look at – just when you look at back of the pockets or back of the envelope calculations, if all you had done (inaudible) to volumetric change, you would’ve said okay, just because of that thermal expansion coefficient of the polymer, the polymer does not look like the way to go because you’ve got a very high thermal expansion coefficient, if I run that into biometric changes you’ve got three times alpha, so there’s your roll right here, we’d have a fourfold increase in that volumetric expansion.
But if I convert that back to a force on the actual system because the modulus is so much stiffer for the polymer versus the metal, you end up equalized in terms of the actual forces. So your gut might have been to say, oh, four times the strain, I am going to expect to see a much greater contribution on stress or force. So just little plays on how some of these relationships work. So polymers because they have a lot of modulus make them very forgiving materials in lot of these applications. Question?
Question: Can you explain why you subtracted the alpha of enamel?
Lisa Pruitt: Because you’re looking at the differential of thermal expansion. So you’re looking at what’s the overall change. So you’re assuming at the boundary, the thermal expansion difference between how much – in other words, the thermal expansion is going to occur in the resin but it’s going to also have a temperature effect that’s going to be balanced by what’s going on in the enamel itself. So if you add delta T, you don’t just have the resin expanding, you also have contribution of what your dental tissue is doing as well. So you subtract that away. The same question, okay. Yeah, so we subtract out the counterpart, so we subtract that away because it’s also experiencing a thermal expansion effect.
So again that was very simplistic approach, just taking a simplistic strain, looking at how we can convert that to a simple force but it gives you perspective of just something we would design for differently in dental applications that we would never see in any of the other materials. So delta T issues are an issue.
So if we look at just some of the environmental effects, chewing forces, I think when you first think about dental applications, you don’t tend to think of the forces in the mouth being very high. And the forces in the jaw are extraordinarily high and if you look at [the bright] enamels, you can get extraordinarily high because it relies on their mechanism for prey and predatory effects. But just for a human a chewing force can be up to 900 Newtons. And so you’ve got a high cyclic loading capability. You can have large temperature differences. So we talked about 37 C being the sub-point and here in the mouth you’re looking at potentially a 50 degree C range. So you can run that through and not just singularly in one day but multiple times a day. So you just think about that effect of having something very, very cold, or something very, very hot and probably every one of you has done that, right, at some point, you’ve had something very cold and very hot or vice versa and you probably get a little tinge of nerve response when you did so. So there’s truly a thermal expansion that occurs and you can actually feel that right down to the innervated part of the tissue.
Large pH differences, so again enormous bodies of literature on the role of pH and the role of different types of a composition of saliva in various foods and how that plays a role of pH in the mouth. And it sounds silly, but it makes an enormous difference, large variety of chemical compositions from food, so I am sipping on my — we all have — some of us have coffee, some of us are chewing gum, we’re all loading our teeth in one way or another. So lots of issues.
Going back to what I started with, you’ve got a number of parameters to think about, you’ve got cyclic loads. So we have to think about fatigue resistance, when designing for these TMJ designs there’s a number of issues. There is overall fracture. So you’ve got a post-scenario, so you wouldn’t want to have fracture of the device. You’ve got again a bearing combination. So you’ve got metal on polymer, so we need to be thinking about wear assistance. You’ve got metal that’s now going to live in the presence of saliva, low pH, so you’ve got moisture, temperature and pH issues. So, you’ve got a big-time corrosion problems. And if we thought we had a corrosion design issue when we got to the Morse taper, you stick something in the mouth and talk about having crevice corrosion issues, you’ve got some design standards to worry about.
Disease and Biological Dentistry P2
Let’s talk about bacterial endocarditis. So bacterial endocarditis is an infection of endocardium affecting the inner lining of the heart and its valves, mainly the valves. Now is bacterial infective endocarditis that rare? Well, it’s hard to say because it isn’t seen and it is not diagnosed that often. Now here’s a more broader definition of bacterial endocarditis rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever, nowadays you don’t hear about that much either, right? It’s an acute inflammatory complication of this strap bacteria, and it affects the joints, the brain and the heart, right, because it’s followed — it’s characterized by arthritis, chorea against central nervous system distress and Carditis, heart pain. So with residual heart disease as a possible sequel event.
So this is usually after dental drilling or some kind of trauma or like that the patient comes home and they get severe flu and then they go to the doctor and they are diagnosed with rheumatic fever. So what did Weston Price say that the two worst things were in life in regard to stress to our immune system? What were the two worst challenges in life? Divorce and death. You’re close. So Dr. Price said the two biggest challenges to our immune system in life are pregnancy, it’s a big deal, a woman has to really be taken care of, nourished, and flu for he lived through the 1918 flu. But this is what this rheumatic fever is. It’s characterized by like flulike symptoms which are sometimes diagnosed as rheumatic fever often missed.
Rheumatic disease just to review, this is any disease of streptococcal bacterial origin. Now again this used to be a lot more common and talked about in the 1950s, 1940s but then when antibiotics came in, as soon as you gave an antibiotic, yes that did reduce the symptoms. So it’s not talked about so much. But we know what the antibiotics do, they kill some bugs, other ones cause later problems. So as biological dentists and physicians and practitioners, we know about silent focal infections. That’s why I love this group because we’re very aware of these chronic silent focal infections that conventional dentists and doctors aren’t aware of at all and sadly, holistic practitioners and physicians aren’t very aware of at all.
So what are typical focal infections? The dental tonsils, sinus, genital, other foci, and what do these focal infections do? They are chronically like a machine generating pathogenic bacteria and they are going to migrate and metastasize typically to what’s called rheumatic disturbed fields in the body, rheumatic streptococcal related places that make a happy home for strep bacteria where strep bacteria like to live. And there are five main rheumatic disturbed fields. First of all, the heart, again the endocarditis to the valves, rheumatic fever includes all of these — three of these areas. Joints chronic rheumatoid arthritis, kidney’s acute chronic glomerular nephritis, the gut, appendicitis, stomach duodenal ulcers, and we already talked about the brain. In the old days they called it chorea, nowadays we call it Tourette’s. It’s really the same thing.
It is interesting Tourette’s was diagnosed or identified by a Frenchman Tourette in an 86-year-old woman in the 1880s, unusual? Because nowadays we see it in children and teens and usually after that except for 10% of the time the patient adapts and it’s not so obvious those kind of symptoms or they grow out of it as they say. PANDAS, Grandas and then this whole epidemic of ADD, ADHD, hyperactivity in kids, all manifestations of strep bacteria. So I want to mention Edward Rosenow. Who knows Edward Rosenow? Such an amazing man and if you do get my book, I hope you will read that history as well (inaudible) to my next book the price of root canals, the turn of the 20th century was just amazing. That was just the hallmark, that was the time of focal infection theory that was just exploding, and we had an incredible research that — doing root canals became such a thing, giving antibiotics in the ‘30s and ‘40s, which was huge backlash to that and then it all died. And we are the ones taking up the reins on that and telling people, yes, focal infections are real, we have to address them. You can’t diagnose what you don’t know about and treat.
So Rosenow was considered a research genius. Later Mayo Institute recruited him because he was an amazing biologist, amazing man and he found that streptococcal bacteria loved this partial tension of oxygen, they don’t like anaerobic areas without oxygen, they don’t like aerobic areas, they like this partial tension of oxygen. And also that streptococci along with that had a specific pathogenic affinity for certain tissues. Well, what are those certain tissues? They love the heart valves. Again that’s a partial oxygen environment, mitral valve first, aortic valve, second, very common for patients to come in with some kind of diagnosis of mitral valve disease, minor or moderate or significant, usually minor to moderate, it’s a very common finding in what it is strep bacteria metastasizing to that heart valve. And it can be mitral valve prolapse, stenosis or more serious regurgitation.
The strep bacteria also love the joints, they love the joint capsule, that synovial fluid, very warm, nice, happy little environment for them. That’s why we have so much arthritis, again partial tension of oxygen partly oxygenated, same thing with the kidney glomeruli, same thing with the frontal cortex in the brain, all these tissues are very good areas for the Streptococcus to live and to thrive. So Rosenow did this same research that Dr. Price did too and we all know this research that Dr. Price in Cleveland, Rosenow was at Rush medical College in Chicago. Dr. Price was in Cleveland, there was a lot going on in the Midwest. Midwest was really popping band with all these scientists studying focal infections. So Dr. Price put together a team of 60 leading scientists, what an amazing man and that included Dr. Milton Rosenau, not the same one of Harvard Charles Mayo or Rochester, we know what he ended up doing at Mayo clinic. Dr. Frank Billings of Chicago at Rush medical College who also — that’s where Rosenau worked and what he would find is, if he took an infected tooth and infected root canal tooth from a patient with heart disease and pulled that tooth, extracted it, cavitated it well I hope and then he put it under the skin of a rabbit that would develop the same disease, whether it was ovarian disease, pelvic inflammatory disease, heart disease, skin disease, anything. So it was so well correlated. It was amazing. It is almost like that strep bacteria had grown to that particular affinity and then it would want to go to that same place in that animal, right? I was in a joint before, I’m going to go to a joint again, wanted to find a home again, right?
So I know a lot of you know about Price’s research on this and a lot of other doctors did research and found the same issue. Now later on detractors which we are feeling because this focal infection theory isn’t popular nowadays. Detractors tried to do the same thing other scientists did and they didn’t do it properly. They didn’t put the strep bacteria, they didn’t keep it in a partial oxygen environment. They said [it isn’t true]. So you have to do the research correctly.
So let’s talk about focal infection parlance, I got to see tons of old friends here. Maybe some of you are new and don’t realize that our biological demo group, we’re very into vocal infections, the diagnosis and treatment of those. So the two main ones of course the teeth and the tonsils, that’s the cause, okay, and the disturbed fields is the area, the rheumatic field area like the heart valves or the hip joint or the kidneys or the brain. So if you have an impacted wisdom teeth, often those are silent with intermittent little pain and swelling. You are not even thinking about your heart. Or if you have a root canal infected or if you have an abscessed tooth or if you have incompletely extracted wisdom tooth. In the focal infection site there all of these areas continually generate bacteria and go to susceptible areas in that patient and of course the patient — there’s also the patient’s miasm, right, or condition or heredity, but really those of us that know about epigenetic nowadays that it’s really not the genetics itself, genetics is really only 5 to 10% of the time the problem. Epigenetic says you can completely change your life based on your environment. You don’t have to be prone to heart disease just because your family was or your ancestors were.
So I love this quote from Dr. Price, modern medicine is mistaking effect for cause. Modern medicine is mistaking effect for cause. So as we said this may be a new slide – no, do you have this in your slide? Okay, sorry, I added a few new slides. So I just love this quote, treating a patient’s joint or heart disease without examining the strong possibility of a focal infection in the teeth or tonsils, when doctors are doing that they are treating the effect, the symptom, rather than the true cause of the problem, the focus. Now the problem is patients come to us and talk about their hip joint or their heart pang. They don’t come into you guys that know about dental focal infections. They’re just talking about teeth.
So as biological physicians and practitioners we – the teeth information as biological dentists, you all need to list it as you do the whole systemic history, the whole history on what’s going on in the body. But this is so important, meaning that as biological dentists and physicians we’ve got to treat upstream, not just downstream. We’ve got to treat the cause and dental and tonsil focal infections are epidemic, every single one of you in this room probably has one or the other.
Now [Spransky] was a renowned Russian physiologist and he talked about this trigger factor and he was saying that chronic relatively silent dental focal infections can flare up from the second insult and I just added as dental cleaning, drilling, extractions. So again what we don’t want to do when we have this bacteremia in the bloodstream is that we don’t want to trigger a dormant heart disturbed field and be part of the cause of a heart attack in three weeks or triggers more bacteria to load onto the patient who already has existing dental and tonsil focal infections, already has a lot of bacteria on board. So what can we do? So silent heart disease, little bit more about the mitral valve, the mitral valve is the main valve that gets injured. This is very common mitral valve disease. It’s the most commonly disturbed and infiltrated and infected valve than the heart, the second is the aortic, third tricuspid.
Now again heart disease even though it’s a disturbed field and we’re saying disturbed fields are usually symptomatic. This disturbed field is usually rather asymptomatic patients. Sometimes they have palpitations, shortness of breath, apnea, angina, heart pain and fatigue but often this deposition of strep bacteria causes very little symptoms. Mitral valve disease, rheumatic heart disease without a history of rheumatic fever, well as we said rheumatic fever flu gets missed all the time depending how strong the symptoms, often undiagnosed, or you take antibiotics prophylactically and you just never know you have it, which some people will say, well that’s good but there are better choices.
Infographic: The Best Homemade Toothpaste
The Dangers of Mainstream Dentistry P3
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: you can get it all day long. If you’re a nurse, great. You can get it and IV yourself. If you’re not a nurse and know a nurse maybe you can get the nurse you know to IV. by the way you don’t have to have , unless you’re having figuration of the hear , you don’t java to have IV at the time you’re getting the dentistry. You walk out and put the IV in. that would have taken care of its potential infection like this, without hurting him in the process.
I only know two dentist that will only do it to people they know in the whole United States. We probably have 3,000 dentist in the United States and I only know two. I spend a lot of time questioning and talking to people about this stuff. I don’t know who you’re going to find they may be somebody here, you may also want to find a nurse. IV is pretty easy to give you.
When they pull it out make sure you have a competent dentist because if they pull it out and leave fragmentation in it’s still not going to drain. When I had mine removed I could actually feel eight months later and taste eight months later infection coming out of my mouth. I had on and off pain consistently up in the jaw it would become sensitive or become numb. It really took three months before that went away and eight months before the test went away. That’s bacteria coming out of your body.
The bridge is not going to prevent that from draining. The key with the bridge is that you want a complete composite. You don’t want nickel on the bridge. A cheap bridge they will put nickel on than you won’t have your problem but you’ll have rashes.
The white fillings are called composite. Gold fillings are better than mercury fillings but still they put electromagnetic frequency in the body. We should get rid of past, we should get rid of tooth brushes. Be everyone starting today should get a water picker device called a water cleansing mouth device.
In that device you’ll put some of the period liquid. Not only is it stimulating blood, cleaning better than possible but it’s also disinfecting the mouth.
Audience: I have a root canal. I’ve got an abyss now on my gum. they told me to take garlic, I’ve been told to take the antibiotics, I’ve been told to take some grass seed as well but if I’m going to get it extracted now what’s the preparation for extraction ?
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: very similar, you fast but in this case have you ever fasted before?
Audience: like a juice fast or a complete fast?
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: just juice.
Audience: yes
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: green juices not fruit juices. If you could do it for three days. You can do it the day before, the day of and the day after. Do saunas, do an aerobic exercise. you’re used to fasting , your blood sugar is stable , great time to really perspire a lot . , copies amount of liquid or whatever you weight do double the amount that day and really flush. When we talk about juices we’re talking about sprout justices, green juices not carrot juice and beet juice.
Chlorella not only takes care of heavy metals. It boosts the immune system, corrects the chromosome damage that you’ve done thorough what our lifestyles have caused and equally takes away biology. We can’t say this but there is evidential science and Nadia can explain this to you that it even directly helps cancer in the body.
Audience: is there something you can administer for the pain, like an aesthetic, would you do that to cool your contraction?
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: it depends upon the person. How many of you have high thresholds of pain? Like my wife if you scream and say you’re going to go to a dentist that’s when she needs acupuncture. There’s people with hypersensitivity and if you’re one of those would do it ahead of time.
Audience: when you said about losing memory, I had an emergency operation long ago where I had a lot of aesthetic and since then my memory is rubbish.
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: what was the surgery?
Audience: I had an emergency <inaudible>when I had my child, I was put on epidural. Since then my memory is bad. What can I do about it?
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: let me explain where most of this comes from. anaesthetic is a usual suspect but it has been determine now in the archives of medico that more than 80% of memory loss comes because oxygen didn’t not go to your Bain for a period of time. During the surgical procedure this is common with bi pass surgeries.
There is a cardio vascular aspect to having a cessation. What may have happened is that you stopped breathing, they didn’t get enough oxygen to your brain. All it takes is thirty seconds. If you go above a minute you’re in real trouble, a minute and a half and you’re a real goner.
Audience: what do I do about it?
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: first you need to do oxygen therapy. What we do at hypocrites and what the German have thought the world id so you exercise?
Audience: just walking
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: that’s not enough. At my house I have an elliptical machine. They are much better than running because you don’t have stress on your body. All of the forty year olds and fifty years olds show up at the institute with bad knees, bad aback, arthritis etc. I like no stress exercise and right next to that machine as we have at the hypocrite’s gym we have oxygen condensers.
When people come in they can check it, they get oxygen to their nose and as you’re doing aerobic exercise you clean. Hands down this is by far the best thing I can tell you to do to bring back memory.
Secondly we created a product, I think Melanie has it here called phys-neur oil where you can get it shipped across the pond. I specifically created this for neuron damage in the brain. The number one oil it has in it is cranberry seed oil. All the major work that was done on neuron reconstruction, redevelopment and health recovery shows cranberry seed oil by far up here. Second I have black raspberry, second best and then I put for body and a little bit the brain not as much is some hemp and some flax oil.
Hands down, oxygen to the brain, oil over here. 70% of the population lacks b12. I don’t care if you eat meat, fish, cheese you’re most likely lacking b12. Life give is available here in London and in Europe that’s the one to take.
audience: I’ve got to tell you I’ve got root canal work done almost a year and I’ve got irregular heart beat and irregular breast cancer.
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: tell me what I said boar Germany. 167 000 women, more than 60% had a root canal in one or both of the teeth that related to the breast. When you see a study like that no legitimate doctor or scientist will ever suspect that that’s not a major contributor to breast cancer.
Audience: I recently had a root canal because I have lung cancer but I didn’t have lung cancer before that, I’m not saying that it’s directly related to that. I saw the dentist on Friday he seems to think that maybe it’s something that was <inaudible> and I’m just wondering is it something that takes and forms in six months
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: let me explain what a dentist is. A dentist goes to medical school. They’re literally a medical doctor who has a speciality in dentistry. They really are medical doctors that’s why most of them are still doing bad things to you.
If it is infect what they suspect there’s a 99.9% chance it will come out and so I will let it go its course. If in six months put it on your calendar, then you’ve got to go to somebody to look more. I would do a thermography of we’re talking the end of this year and see if inflammatory things are happening. This is not an x-ray, it’s better than an x ray it picks up heat and inflammation in the body. These a widely used to look at cancer. It’s not common because the pharmaceuticals don’t make money on this.
If you have a problem six months from now it’s probably going to be gone by the end of the summer. The time these things correct is when it’s hot. It should come out naturally. Are you living well?
Audience: yes
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: its nothing to worry about let me put it that way.
audience: I don’t have a question I just wanted to share that I had fillings removed three years ago by a dentist inn London and he’s an incredible doctor who has done more than what he suggested . I told him about thoughts lecture but he’s not here tonight. His name is Doctor El-Gassaway. I think his website is holisticdentistry.com. If you Google those key words. He is an amazing individual. He’s the most caring person I’ve ever met and he’s passionate about what he does.
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: let’s imagine that some of these people are not economically endowed is he the kind of guy you can go to?
Audience: yes he is extremely generous from his heart. He’s on Harley’s Duke. He’s been doing this for a very long time and what brought him in to this is that he was a big <inaudible> and so t just became his life and passionate.
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: that’s a great suggestion. These are the kind of doctors I love. They had the disease, they had the problems. They become missionaries for these stuff. The best doctors are like that when they reverse the disease.
Audience: I had a root canal done by a Marian <inaudible>. He’s an amazing dentist. I always felt that ever since something was not right. so my question is I still have all my teeth , unfortunately now I know it’s not so great but I do have probably at least 3 or 4 root canals and they’re all fine. Now I know this isn’t right. Is there any chance for me to have them re opened and closed properly?
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: remember the guy I talked about with the space suit that’s the kind of thing those people do. most dentist and even I were an alternative dentist I probably wouldn’t do it because if I reopen a tooth that has an infection in it the susceptibility of getting a grand infection is heightened. Pulling it would be a better route.
Audience: I have a question, with all the natural approaches and the fact that they heal and the body is so extraordinary. How is it that there is this one area in our body that can’t take care of its self?
DR BRIAN CLEMENT: it’s an interesting thing. It’s probably the most abused part of the human anatomy. There’s nothing more abused than the mouth. If you think about what we’ve done with our mouth. When I look back and my wife and were sitting and looking at thousands of people swabbing their mouths and saying how come we haven’t had that.
We realize that it must have been in the natural state of affairs. That the human body devolved and not evolved into allowing spiral k and bacteria to prominate and to live in that area.
Secondly look at what we’re eating. Most health food diets are incredibly high in sugar. let’s imagine that you’re the rare person who says I’m not going to take honey , I’m not going to take maple syrup, I’m not going to take white sugar but I’m still going to eat bread and potatoes and pastas. Guess what you’re getting sugar around the bout ways. I eat things that will create sugar in my mouth. All of these things are going to fee d what we have devolved our bodies into having, this bacteria states, these spiral k state.
Common Solutions for Lower Back Problems
Whether you are a weekend warrior or a professional athlete there is a chance that you have suffered from some type of back problem in your life. While many times these aches and pains go away quickly, others seem to linger. For those that have these issues we offer simple solutions to help with your back problems.
Whirlpool Treatment: The power of heat is a great solution for those who suffer constant back pain. Not only does the heat warm up your lower back, but it also lets you stretch the muscles. For those who have a gym membership or have access to a hot tub, I would suggest 15 minute intervals with at least 15 minutes of rest in between.
Inversion Tables: One of the best friends for anyone with a back issue is an inversion table. An inversion table lets a person hang upside down to fix their back issues. One thing is that not all of these tables are the same and that is why it is recommended to get an inversion table review online before purchasing one of these great tools. Teeter Hang Ups and Ironman are just a few of the most popular models that get great reviews.

Stretching Exercises: We recommend stretching exercises for people who have enough flexibility to hold a stretch for at least 45 seconds. We don’t recommend certain stretches if one has a back problem where they can’t bend down without extreme discomfort.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture is a great tool for those who have had constant back pain and are looking for an alternative solution. Many professional athletes have added weekly accupuncture to their regime as it helps keep them loose and ready to play.
Ice Treatments: Ice can be a best friend to those looking to heel quickly after a back injury. It is necessary to use ice in shifts like you do a whirlpool as too much ice at one time will not help. Ice, Rest, Ice, Rest is a common strategy for those looking to heel an ailing back.
Having a lower back problem is something that almost all of us have had at one time or another. With that being said, the following tips above can help you fix those problems in no time.
